Which Materials Can Be Used For Making Gaskets?
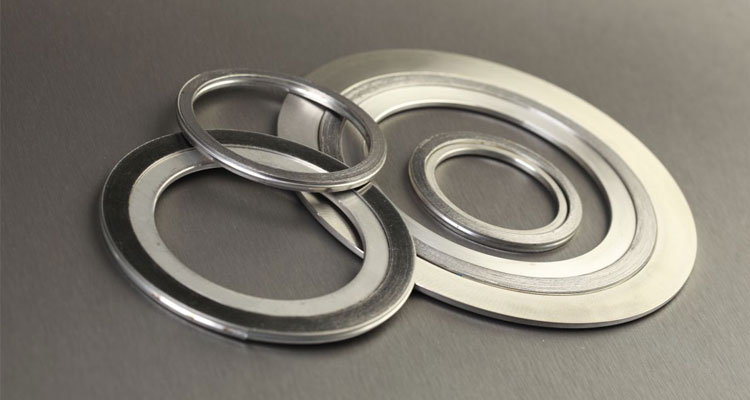 The main aim of a gasket is to create and retain a stagnant seal between two stationary parts and containing a fluid/gas by blocking any potential leakage path, and protecting the immediate environment from contamination. While preventing the passage of the fluid, the gasket must be able to fill any irregularities in the mating surfaces being sealed, while also being sufficiently resilient to resist extrusion under operating conditions. A variety of materials are used by spiral wound gasket manufacturers in India to manufacture gaskets, which are divided into three main categories, namely metallic materials, elastomeric materials, and fibrous materials, about which we will learn individually in this blog.
The main aim of a gasket is to create and retain a stagnant seal between two stationary parts and containing a fluid/gas by blocking any potential leakage path, and protecting the immediate environment from contamination. While preventing the passage of the fluid, the gasket must be able to fill any irregularities in the mating surfaces being sealed, while also being sufficiently resilient to resist extrusion under operating conditions. A variety of materials are used by spiral wound gasket manufacturers in India to manufacture gaskets, which are divided into three main categories, namely metallic materials, elastomeric materials, and fibrous materials, about which we will learn individually in this blog.
Metallic materials
The various metallic materials used for making gaskets include –
- Carbon steel 316, 316L, 304, 304L, 321, 347, and 410
- Alloy 200,400, 600, 625, 800, 825,B2, and C276
- Titanium, Aluminum, and Copper
Elastomeric materials
These materials are made in various compositions and are available in specification grade and commercial qualities. They generally are used as binders when combined with various other fibers and fillers. The list of elastomeric materials that can be used for gaskets include –
- Natural Rubber, which is resistant to mild acids and alkalis, and inorganic salts; and has excellent recovery properties. However, it is not recommended for oils, solvents, or exposure to oxygen, ozone, or sunlight.
- Silicone, which has excellent temperature properties, and is unaffected by sunlight and ozone; but unsuitable for steam and hydrocarbons.
- Nitrile or NBR, which has good resistance to oils, hydrocarbons, and temperature capabilities; but not suitable for chlorinated hydrocarbons, ketones, esters, and strong oxidizing agents.
- Neoprene/Chloroprene, which has excellent resistance to moderate acids, alkalis, salt, petroleum, oils, fuels, ozone, and solvents; but not resistant to strong acids and hydrocarbons.
- Fluoroelastomer, which is highly resistant to acids, oils, aliphatic hydrocarbons, and other corrosive fluids; but is not suitable for applications involving steam, esters, amines, or ketones.
- Butyl Rubber, which offers good resistance to ozone and gas permeation, and is most suitable for applications involving mild acids, alkalis, and esters. However, this material is least resistant to oils and fuels.
- Chlorosulphonated Polyethylene, which possesses excellent resistance against acids, alkalis, and oil; and has outstanding fire protection properties too.
- Ethylene Propylenediene or EPDM, which is resistant to strong acids and alkalis, steam, and ozone; but is not suitable for solvents and aromatic hydrocarbons.
- Styrene butadiene, which is suitable for use with moderate chemicals and weak organic acids, and unsuitable for strong acids, hydrocarbons, and ozone.
Fibrous materials
- Aramid, which offers high strength and stability, with medium temperature suitability.
- Asbestos, which is inert, intoxic, incombustible and a poor heat conductor, and unaffected by temperatures up to 450°C
- Carbon fiber, which has high thermal conductivity and great chemical resistance, but is unsuitable for oxidizing environments.
- Cellulose, which is a natural fiber suitable for low temperature and medium pressure applications.
- Glass, which offers good strength and moderate chemical resistance, and is suitable for medium to high temperature applications.
- Man made mineral fiber or mineral wool, which consists of metal silicates, and is suitable for medium to high temperature applications.
Other than the above mentioned materials, there are three other very popular materials used to make gaskets, which cannot be categorized into metallic, elastomeric, or fibrous materials; and these are –
- Flexible graphite, which has good chemical resistance and is suitable for exceptionally wide temperature ranges between 400-2500°C.
- Mica, which possesses high flexibility, elasticity, toughness, chemical resistance, and thermal stability.
- PTFE, which has extremely strong chemical resistance, high compressibility, low permeability, handling ease, excellent anti-stick and dielectric properties.
Whatever your choice from the above, you can get all sorts of metallic, non-metallic, and semi-metallic gaskets made from the best quality materials from Trim Engineering Services, one of the leading and most reliable spiral wound gasket manufacturers in India.