Can Overheating Affect Gasket Performance?
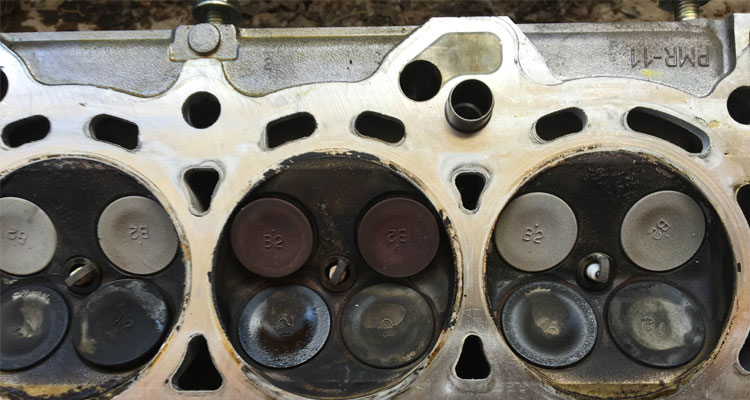 Gaskets are those tiny elements that seal the space between two mating surfaces to prevent leakage from and into the joined objects while under compression. Gaskets are used in a variety of applications around the world; some of them being high temperature, high pressure applications like steel mills, petro-chemical stations, power generation stations, high-pressure pumps, heat exchangers, steam lines, and chemical reactors. The most important consideration for these types of applications is the selection of an appropriate gasket material. The wrong material could result in leakage, equipment failure, combustion, or even workplace injury. This is why high temperature gasket materials like graphite, silicone, fluorosilicone, ceramic, fiberglass, and PTFE are used for such applications to avoid potential harm and damage.
Gaskets are those tiny elements that seal the space between two mating surfaces to prevent leakage from and into the joined objects while under compression. Gaskets are used in a variety of applications around the world; some of them being high temperature, high pressure applications like steel mills, petro-chemical stations, power generation stations, high-pressure pumps, heat exchangers, steam lines, and chemical reactors. The most important consideration for these types of applications is the selection of an appropriate gasket material. The wrong material could result in leakage, equipment failure, combustion, or even workplace injury. This is why high temperature gasket materials like graphite, silicone, fluorosilicone, ceramic, fiberglass, and PTFE are used for such applications to avoid potential harm and damage.
How does heat affect gasket materials?
In the above mentioned high-temperature applications, or any other similar situations, hot water and hot steam stream down restricted channels, looking for an exit. The energy generated then attacks the intermingled seals within the hot pipelines. The effect of this thermal release can be extremely disastrous. It could include swelling, hardening, and material changes that destroy the structural integrity. And, when adverse temperatures prevail such that the thermal energy dispersed is more than the toleration level for the gaskets used, the mechanical asset degrades dramatically! The material of the gasket begins to bake, thus leading to hardening and loss of elasticity. With rise in this thermal exposure, the hardened gasket is likely to crack and break, leading to leakage.
The above scenario explained is just a generalization. Realize that different materials and different situations react differently to extreme temperature conditions. Excessive thermal energy is no doubt destructive in every aspect, but its effects differ according to the materials used in each application. For example, plastic variants melt and deform; setting materials tend to shrink and harden, thus leading to cracks; and creep and relaxed fits loosen the tight flange with the deformation of the material. However, in any case, the result is leakage.
Therefore, you must select strong engineered plastics or metal-reinforced materials to avoid performance-weakening occasions. The best materials are thermally capable plastics and deformation-resistant alloys that don’t contract or expand, or harden or become brittle. In fact, these materials always stay intact, no matter how hot the application or procedure becomes.
Why should you choose Trim Engineering Services’ gaskets?
Trim Engineering Services is one of the best spiral wound gasket manufacturers in India. But, it manufactures all sorts of metallic, non-metallic, and semi-metallic gaskets.
Metallic gaskets – As the name suggests, these gaskets are made with a single or combination of metals that are suitable for high pressure and high temperature applications. The most common materials used include stainless steel, aluminum, brass, carbon steel, copper, lead, nickel, bronze, and titanium.
Non-metallic gaskets – These gaskets are made from materials that compress easily, but are limited in the temperatures that they can handle. The most common materials used include Nitrile (-51 to 121°C), EPDM (-57°C to 177°C), silicone (up to 260°C), and PTFE (up to 232°C).
Semi-metallic gaskets – These gaskets comprise of metallic windings and non-metallic fillers; thus bridging the gap between metallic and non-metallic gaskets. These gaskets are used in high temperature and high pressure applications. the most commonly used materials for metallic windings include stainless steel, and for filler materials include asbestos and graphite.